01. Proton Therapy Overview
What Is Proton Therapy?
Proton therapy, or proton beam therapy, is a type of external beam radiation treatment that may be used to treat some types of mesothelioma. It delivers high doses of radiation to the tumor. The radiation damages cancer cells and keeps them from growing.
The treatment may use 3-D imaging scans to help doctors target the tumor. Using 3-D images allows doctors to direct radiation to targeted cancer cells while causing less damage to healthy ones. Because of this, proton therapy may have fewer side effects than traditional radiation therapy.
Researchers have studied proton therapy for other cancers since the 1950s. The Food and Drug Administration approved proton therapy as a treatment option for some cancers in 2001. However, very few radiation oncology departments have proton therapy available because it requires expensive equipment.
Researchers continue to study this cancer treatment for mesothelioma through clinical trials. As the trials finish, the emerging therapy may become available in more cancer centers.
02. Proton Therapy for Mesothelioma
How Does Proton Therapy Treat Mesothelioma?
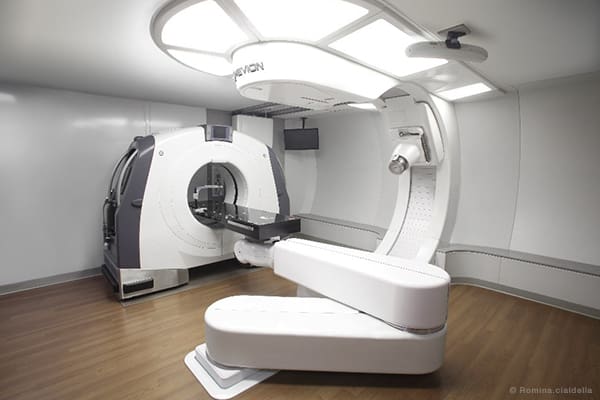
A machine separates the protons from hydrogen atoms and speeds them up. Large magnets in the machine direct the protons through the body to the tumor. The beam of protons is narrow and can adjust to control where its energy is released. This means it damages fewer healthy tissues.
Proton therapy for cancer treatment works by damaging the DNA in cancer cells. The protons release a high amount of radiation energy. This energy breaks DNA strands, disrupting cancer cells’ ability to repair themselves. This keeps them from growing or creating new cells.
Clinical trials continue to examine how well proton therapy can work for mesothelioma treatment. Two completed clinical trials show proton therapy may increase survival for some patients. However, these studies had only a few participants. A third study started late in 2023.
Researchers have not focused on proton therapy for peritoneal mesothelioma. While beneficial for pleural patients, radiation has not worked well for peritoneal patients.
Proton Therapy Procedure
The proton therapy procedure has three phases. Generally, patients will have a preparation, treatment and recovery phase. The three phases together can last months.
- Preparation stage: This stage may take several weeks on its own. The patient undergoes imaging scans to confirm the tumor’s size and location. The care team then uses those images to determine the best position for the patient and the correct dose. Sometimes, the care team makes positioning aids to help the patient hold still during treatment. They may also mark where the tumor is on the patient’s skin with a pen.
- Treatment stage: First, the patient gets into position on a table with the help of the care team. Next, the oncologist lines up a large mechanical arm called a gantry. This arm can move around the patient and deliver radiation from different angles. Then, the patient has an X-ray to ensure everything is lined up. Finally, the care team leaves the room, and the treatment begins. Each treatment may take around 30 minutes. Patients may have five treatments a week for several weeks.
- Recovery stage: Most people can go home and do their usual routine activities after treatment. Adults can often drive themselves to and from their appointments unless they were sedated for the procedure.
It’s important to note that each procedure is unique to the patient. The care team can answer questions specific to your case.
Resources for Mesothelioma Patients
03. Benefits & Disadvantages
What Are the Benefits and Disadvantages of Proton Therapy?
Proton therapy presents both advantages and disadvantages. Doctors have found most of the benefits when treating other cancers, like breast and prostate. These benefits may also help mesothelioma patients. Possible benefits include:
- Fewer side effects: Proton therapy may cause fewer and more mild side effects than traditional radiation.
- Less damage: Traditional radiation may damage other organs in the thoracic cavity, like the lung or heart. When used to treat mesothelioma, proton radiation precisely targets the treated area. It sends a thin beam to the tumor and may not damage as much healthy surrounding tissue.
- Targeted: The treatment is a highly targeted radiotherapy, which may be a significant benefit. It allows doctors to deliver higher doses of radiation to the tumor. It may also reduce the risk of developing secondary cancer caused by radiation.
Unfortunately, proton therapy does have some drawbacks. These disadvantages may include:
- Insurance coverage: Not all insurance companies will cover proton therapy. They may want proof that it is a better treatment for the patient’s cancer.
- Limited availability: Few cancer centers have the equipment to perform the procedure. Those with it often cannot treat as many patients due to limited time for scheduling. It also means patients may have to travel to get treated.
Mesothelioma doctors can explain specific advantages and disadvantages of proton therapy to patients.
Proton Therapy and Mesothelioma Survival
Not enough research exists to show how proton therapy for mesothelioma may improve survival rates. As researchers complete more clinical trials, more data may become available.
A study has shown positive results for patients with inoperable stage III lung cancer. In the study, patients received proton therapy with chemotherapy. They had a median survival of 26.5 months. The authors compared this to older data from patients who received standard treatment. The median survival was 16 months for patients receiving chemo and traditional radiation. So proton therapy may have extended survival by more than 50%.
Proton therapy has been part of two small studies for mesothelioma. These studies included proton therapy as part of a multimodal treatment plan. Results showed improved survival with patients living up to 2 years.
More research is needed to determine if proton therapy will benefit mesothelioma patients.
04. Side Effects
What Are the Side Effects of Proton Therapy?
Proton therapy for mesothelioma may have fewer side effects than traditional radiation. In general, it does not have the same level of toxicity as traditional radiation. But patients receiving it have still reported side effects. These side effects may be different for mesothelioma patients.
Researchers need to study this treatment more to understand which side effects may affect mesothelioma patients. Even so, patients can speak with their care teams about what to expect. Doctors can also help manage side effects if they do arise.
05. Eligibility
Who Is Eligible for Proton Therapy?
Proton therapy is still considered an experimental therapy for mesothelioma, and doctors do not have established guidelines for eligibility. But some people with pleural mesothelioma may be eligible for proton therapy.
Pleural mesothelioma patients who are receiving therapeutic radiation might qualify for proton therapy. These patients may benefit because proton therapy delivers less radiation to the healthy lung.
Some notable cancer centers with a proton therapy center include:
06. Common Questions
Common Questions About Mesothelioma Proton Therapy
-
What are the key benefits of proton therapy for mesothelioma patients?
- Proton therapy for mesothelioma may offer benefits to some pleural mesothelioma patients. Proton therapy uses a targeted beam of high-dose radiation. This targeting may mean less damage to surrounding tissues and fewer side effects. A higher dose of radiation may have better results.
-
What is the success rate of proton therapy for mesothelioma?
- Researchers have not studied proton therapy for mesothelioma very much. Two completed studies suggest survival was between 4 months and 2 years. However, these studies included few patients. The data may be unreliable. A pending clinical trial includes a large group of patients and may provide more reliable data.
-
What stage of cancer is proton therapy most useful for?
- Depending on the type of cancer, doctors may recommend proton therapy. For example, proton therapy may be used in any stage of prostate cancer. However, it may not work well for cancers that have spread (metastasized). Your oncologist can answer specific questions about your individual case.